Functions | |
| I32 | gauss (image *src, image *dst, F32 sigma) |
| Gauss Filter (Recursive Version). More... | |
| I32 | gauss_hor (image *src, image *dst, F32 sigma) |
| Horizontal Gauss Filter (Recursive Version). More... | |
| I32 | gauss_ver (image *src, image *dst, F32 sigma) |
| Vertical Gauss Filter (Recursive Version). More... | |
| I32 | gauss_fir (image *src, image *dst, F32 sigma) |
| Non-Recursive Gauss Filter (FIR). More... | |
| I32 | boxavg (image *src, image *dst, I32 kx, I32 ky) |
| Averaging Over a Rectangle. More... | |
| void | ii_boxavg (image *integral, image *dst, I32 kx, I32 ky) |
| Integral Image Based Averaging Over a Rectangle. More... | |
| I32 | avg (image *a, image *b, I32 kx, I32 ky, void(*func)(), I32 v) |
| Moving Average or Unsharp Masking of an Image Variable. More... | |
| I32 | avg2 (image *a, image *b, I32 kx, I32 ky, void(*func)(), I32 v) |
| Moving Average or Unsharp Masking of an Image Variable. More... | |
| I32 | isef (image *src, image *dst, F32 b) |
| Infinite Symmetric Exponential Filter (Recursive Version). More... | |
| I32 | isef_hor (image *src, image *dst, F32 b) |
| Horizontal Infinite Symmetric Exponential Filter (Recursive Version). More... | |
| I32 | isef_ver (image *src, image *dst, F32 b) |
| Vertical Infinite Symmetric Exponential Filter (Recursive Version). More... | |
| #define | avgm(a, b, kx, ky) avg(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())0, 0) |
| Moving Average. More... | |
| #define | maskx(a, b, kx, ky, v) avg(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())FL_sub2x, v) |
| Unsharp Masking of the Image. More... | |
| #define | masky(a, b, kx, ky) avg(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())FL_sub2y, 0) |
| Unsharp Masking of the Image. More... | |
| #define | avgm2(a, b, kx, ky) avg2(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())0, 0) |
| Moving Average. More... | |
| #define | maskx2(a, b, kx, ky, v) avg2(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())FL_sub2x, v) |
| Unsharp Masking of the Image. More... | |
| #define | masky2(a, b, kx, ky) avg2(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())FL_sub2y, 0) |
| Unsharp Masking of the Image. More... | |
| #define avgm | ( | a, | |
| b, | |||
| kx, | |||
| ky | |||
| ) | avg(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())0, 0) |
The macro calculates the moving average filter of image variable a and stores the result in image variable b. kx and ky are the horizontal and vertical kernel size. More information at avg().
The result image will be centered according to the kernel size (kx, ky), i.e. the (smaller) result image will start at location b->st + kx/2 + (ky/2) * b->pitch.
avgm() is a macro which calls avg() with basic function void(*)() 0 as an argument.
| #define maskx | ( | a, | |
| b, | |||
| kx, | |||
| ky, | |||
| v | |||
| ) | avg(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())FL_sub2x, v) |
The macro calculates a so-called unsharp masking of image a to image b. kx and ky are the horizontal and vertical kernel size used to blur the image (moving average). The offs raises the resulting grey value given by that formula: b = clip(0,255, [a - avgm(a) + offs]). More information at avg().
The result image will be centered according to the kernel size (kx, ky), i.e. the (smaller) result image will start at location b->st + kx/2 + (ky/2) * b->pitch.
maskx() is a macro which calls avg() with basic function FL_sub2x() as an argument.
| #define masky | ( | a, | |
| b, | |||
| kx, | |||
| ky | |||
| ) | avg(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())FL_sub2y, 0) |
The macro calculates a so-called unsharp masking of image a and binarizes it to the image b. kx and ky are the horizontal and vertical kernel size used to blur the image (moving average). The output will be given according to that formula: b = ([a - avgm(a)]>0)?(255):(0). More information at avg().
The result image will be centered according to the kernel size (kx, ky), i.e. the (smaller) result image will start at location b->st + kx/2 + (ky/2) * b->pitch.
masky() is a macro which calls avg() with basic function FL_sub2y() as an argument.
| #define avgm2 | ( | a, | |
| b, | |||
| kx, | |||
| ky | |||
| ) | avg2(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())0, 0) |
The macro calculates the moving average filter of image variable a and stores the result in image variable b. kx and ky are the horizontal and vertical kernel size. More information at avg2().
The result will be placed in the left upper corner of b.
avgm2() is a macro which calls avg2() with basic function void(*)() 0 as an argument.
| #define maskx2 | ( | a, | |
| b, | |||
| kx, | |||
| ky, | |||
| v | |||
| ) | avg2(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())FL_sub2x, v) |
The macro calculates a so-called unsharp masking of image a to image b. kx and ky are the horizontal and vertical kernel size used to blur the image (moving average). The offs raises the resulting grey value given by that formula: b = clip(0,255, [a - avgm2(a) + offs]). More information at avg2().
The result will be placed in the left upper corner of b.
maskx2() is a macro which calls avg2() with basic function FL_sub2x() as an argument.
| #define masky2 | ( | a, | |
| b, | |||
| kx, | |||
| ky | |||
| ) | avg2(a, b, kx, ky, (void (*)())FL_sub2y, 0) |
The macro calculates a so-called unsharp masking of image a and binarizes it to the image b. kx and ky are the horizontal and vertical kernel size used to blur the image (moving average). The output will be given according to that formula: b = ([a - avgm2(a)]>0)?(255):(0). More information at avg2().
The result will be placed in the left upper corner of b.
masky2() is a macro which calls avg2() with basic function FL_sub2y() as an argument.
The function calculates the recursive gauss filter with filter parameter sigma with 0.0 ≤ sigma ≤ 5.0. sigma defines the equivalent of the filter kernel size (standard deviation) for this recursive filter: The larger the value of sigma, the larger the kernel size. Since this function is designed as a recursive filter, the execution speed does not depend on the size of sigma.
dx*(dy+6)+1) Bytes of Heap Memory. | src | Source Image. |
| dst | Destination Image. |
| sigma | Filter Parameter (0.0 ≤ sigma ≤ 5.0). |
Point spread funtions for different values of sigma (values in Hex):
sigma = 0.625:
![\[ \begin{array}{ccccccccccccccccc} - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & 02 & 05 & 07 & 05 & 02 & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 05 & 0e & 16 & 0e & 05 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 07 & 16 & 23 & 16 & 07 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 05 & 0e & 16 & 0e & 05 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & 02 & 05 & 07 & 05 & 02 & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ \end{array} \]](form_35.png)
sigma = 1.0:
![\[ \begin{array}{ccccccccccccccccc} - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 02 & 03 & 03 & 03 & 02 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & 01 & 02 & 04 & 05 & 06 & 05 & 04 & 02 & 01 & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & 01 & 03 & 05 & 08 & 09 & 08 & 05 & 03 & 01 & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & 01 & 03 & 06 & 09 & 0b & 09 & 06 & 03 & 01 & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & 01 & 03 & 05 & 08 & 09 & 08 & 05 & 03 & 01 & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & 01 & 02 & 04 & 05 & 06 & 05 & 04 & 02 & 01 & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 02 & 03 & 03 & 03 & 02 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ \end{array} \]](form_36.png)
sigma = 1.5:
![\[ \begin{array}{ccccccccccccccccc} - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 02 & 02 & 02 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 02 & 02 & 03 & 03 & 03 & 02 & 02 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - \\ - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & 02 & 03 & 03 & 04 & 03 & 03 & 02 & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - \\ - & - & 01 & 01 & 02 & 03 & 03 & 04 & 04 & 04 & 03 & 03 & 02 & 01 & 01 & - & - \\ - & - & 01 & 01 & 02 & 03 & 04 & 04 & 05 & 04 & 04 & 03 & 02 & 01 & 01 & - & - \\ - & - & 01 & 01 & 02 & 03 & 03 & 04 & 04 & 04 & 03 & 03 & 02 & 01 & 01 & - & - \\ - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & 02 & 03 & 03 & 04 & 03 & 03 & 02 & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - \\ - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 02 & 02 & 03 & 03 & 03 & 02 & 02 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 02 & 02 & 02 & 02 & 02 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & 01 & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - & - \\ \end{array} \]](form_37.png)
| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation Fails. |
| ERR_PARAM | if sigma is not in Range [0.0,5.0]. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
The function calculates the horizontal recursive gauss filter with filter parameter sigma with 0.0 ≤ sigma ≤ 5.0. sigma defines the equivalent of the filter kernel size (standard deviation) for this recursive filter: The larger the value of sigma, the larger the kernel size. Since this function is designed as a recursive filter, the execution speed does not depend on the size of sigma.
| src | Source image. |
| dst | Destination image. |
| sigma | Filter Parameter (0.0 ≤ sigma ≤ 5.0). |
dx+1) Bytes of Heap Memory. | ERR_PARAM | if sigma is not in Range [0.0,5.0]. |
| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation Fails. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
The function calculates the vertical recursive gauss filter with filter parameter sigma with 0.0 ≤ sigma ≤ 5.0. sigma defines the equivalent of the filter kernel size (standard deviation) for this recursive filter: the larger the value of sigma, the larger the kernel size. Since this function is designed as a recursive filter, the execution speed does not depend on the size of sigma.
| src | Source Image. |
| dst | Destination Image. |
| sigma | Filter Parameter. |
dx*(dy+6)+1) Bytes of Heap Memory. | ERR_PARAM | if sigma is not in Range [0.0,5.0]. |
| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation Fails. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
This is the non-recursive version of the gauss low-pass filter (FIR). sigma is the standard deviation of the filter.
sigma | Filter Size |
|---|---|
| 0.391 | 3x3 |
| 0.625 | 5x5 |
| 0.812 | 7x7 |
Values for sigma between the values in the table are allowed. The function switches to whatever filter size comes closer to the value of sigma. The function returns the standard error code.
| src | Source Image. |
| dst | Destination. |
| sigma | Standard Deviation for Gauss Filter. |
| ERR_TYPE | if src or dst Image is no Grey Image. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
This function outputs the arithmetic average of values of pixels lying in a box of dimension (kx,ky) with its output pixel at the center if kx and ky are odd. Data near the image border is extrapolated by repeating the border pixel values perpendicular to the orientation of the border.
| src | Source Image of Type IMAGE_GREY. |
| dst | Destination Image of Type IMAGE_GREY. |
| kx | Horizontal Averaging Pixel Column Count. |
| ky | Horizontal Averaging Pixel Row Count. |
| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation Fails. |
| integral_image() | if not ERR_NONE. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
The arithmetic mean will be calculated using Integral Image Data. The integral image must have the dimensions ( dst->dx+kx, dst->dy+ky) for kx and ky odd. Data is aligned the following way: The pixel at dst(0,0) will contain the mean value over the (1,1)-(kx,ky) square of pixels in the image which was integrated (Average at Integral Image is (0,0)+(kx,ky)-(kx,0)-(0,ky), See Integral Image Theory). You do want to use this function with ImageAllocateEdge().
No validity checks are done!
| integral | Source Integral Image of Type IMAGE_GREY32. |
| dst | Destination Image of Type IMAGE_GREY. |
| kx | Horizontal Averaging Pixel Column Count. |
| ky | Horizontal Averaging Pixel Row Count. |
The function calculates the moving average filter of image variable a and stores the result in image variable b. The size of the moving average is specified with the values kx (horizontal kernel size) and ky (vertical kernel size). Images specified by image variables a and b must be different. If func is NULL, the function will calculate the moving average. If a function address is given, the original image will be subtracted from the moving average, performing an 'unsharp masking' operation.
There is a partner function avg2() which performs the same task using a different output alignment.
For avg() the result image will be centered according to the kernel size (kx, ky), i.e. the (smaller) result image will start at location b->st + kx/2 + (ky/2) * b->pitch.
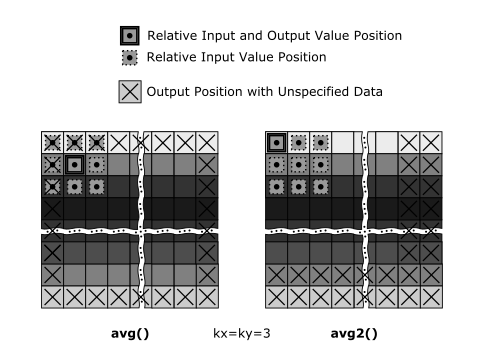
The function pointer passed specifies the type of subtraction being performed.
The return value is negative, if an error is encountered. The following macros are available:
| Macro Call | Result | func |
|---|---|---|
| avgm() | Moving Average | void (*)()0 |
| maskx() | b = (a - avg + offs); clipping if c>255 or c<0 | FL_sub2x() |
| masky() | b = (a - avg)>0 ? 255 : 0 | FL_sub2y() |
Of course, you can write your own subtract functions. Pass their address (function pointer) to avg().
dx/2 + 1) Bytes of Heap Memory. | ERR_FORMAT | if b->dx/y < a->dx/y - kx/y + 1. |
| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation failed. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
The function avg() calculates the moving average filter of image variable a and stores the result in image variable b. The size of the moving average is specified with the values kx (horizontal kernel size) and ky (vertical kernel size). Images specified by image variables a and b must be different. If func is NULL, the function will calculate the moving average. If a function address is given, the original image will be subtracted from the moving average, performing an 'unsharp masking' operation.
There is a partner function avg() which performs the same task using a different output alignment.
For avg2() the result will be placed in the left upper corner of b.

The function pointer passed specifies the type of subtraction being performed.
The return value is negative, if an error is encountered. The following macros are available:
| Macro Call | Result | func |
|---|---|---|
| avgm2() | Moving Average | void (*)()0 |
| maskx2() | b = (a - avg + offs); clipping if c>255 or c<0 | FL_sub2x() |
| masky2() | b = (a - avg)>0 ? 255 : 0 | FL_sub2y() |
Of course, you can write your own subtract functions. Pass their address (function pointer) to avg2().
dx/2 + 1) Bytes of Heap Memory. | ERR_FORMAT | if b->dx/y < a->dx/y - kx/y + 1. |
| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation failed. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
The function calculates the infinite symmetric exponential filter with filter parameter b with 0.0 < b < 1.0. b defines the equivalent of the filter kernel size for this recursive filter: the larger the value of b, the larger the kernel size. Since this function is designed as a recursive filter, the execution speed does not depend on the size of b.
| src | Source Image. |
| dst | Destination Image. |
| b | Filter Parameter. |
dx*(dy+2)+2)/2 Bytes of Heap Memory.| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation Fails. |
| ERR_TYPE | if src or dst Image is no Grey Image. |
| ERR_PARAM | if b is not in Range [0.0,1.0]. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
The function calculates the horizontal infinite symmetric exponential filter with filter parameter b with 0.0 < b < 1.0. b defines the equivalent of the filter kernel size for this recursive filter: the larger the value of b, the larger the kernel size. Since this function is designed as a recursive filter, the execution speed does not depend on the size of b.
| src | Source Image. |
| dst | Destination Image. |
| b | Filter Parameter. |
dx+1) Bytes of Heap Memory. | ERR_TYPE | if src or dst Image is no Grey Image. |
| ERR_PARAM | if b is not in Range [0.0,1.0]. |
| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation Fails. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |
The function calculates the vertical infinite symmetric exponential filter with filter parameter b with 0.0 < b < 1.0. b defines the equivalent of the filter kernel size for this recursive filter: the larger the value of b, the larger the kernel size. Since this function is designed as a recursive filter, the execution speed does not depend on the size of b.
| src | Source Image. |
| dst | Destination Image. |
| b | Filter Parameter. |
dx*(dy+2)+2) Bytes of Heap Memory. | ERR_TYPE | if src or dst Image is no Grey Image. |
| ERR_PARAM | if b is not in Range [0.0,1.0]. |
| ERR_MEMORY | if Memory Allocation Fails. |
| ERR_NONE | on Success. |